Volvo Cars has established a global manufacturing footprint that spans multiple continents, reflecting the company’s evolution from a Swedish automaker to an international brand. Understanding where Volvo vehicles are produced provides insight into the company’s strategic approach to serving global markets while maintaining its commitment to quality, safety, and innovation.
This comprehensive guide explores the countries where Volvo manufacturing plants operate, the models they produce, and how this global network supports Volvo’s vision for the future.
Volvo’s Global Manufacturing Presence: 7 Countries and Counting
Volvo Cars currently operates manufacturing facilities in 7 countries across the globe: Sweden, Belgium, China, the United States, Malaysia, India, and the Netherlands. This international production network enables Volvo to efficiently serve regional markets while maintaining consistent quality standards across all vehicles. Each plant specializes in producing specific models, with some facilities serving as global production hubs for particular vehicle lines.
Quick Facts: Volvo manufacturing plants operate in 7 countries across 3 continents, producing over 700,000 vehicles annually. The company’s oldest plant is in Gothenburg, Sweden (established 1927), while its newest facility opened in Charleston, South Carolina (2018).
Sweden: The Heart of Volvo Manufacturing
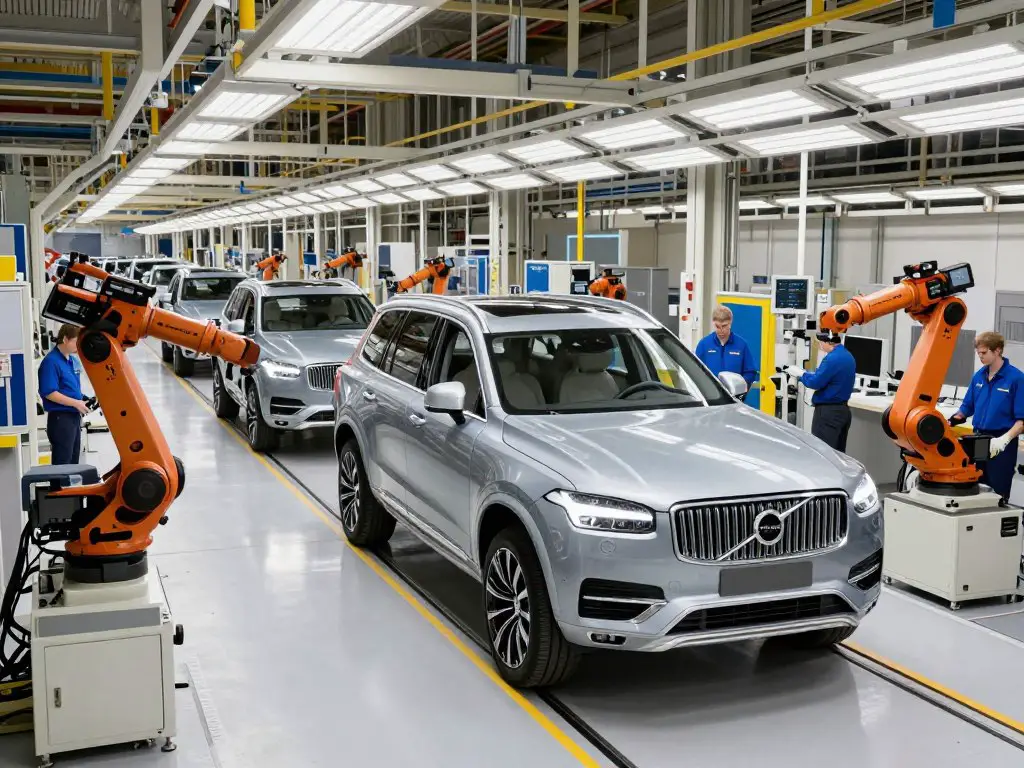

Sweden remains the historical and spiritual home of Volvo Cars, with multiple manufacturing facilities that form the backbone of the company’s production capabilities. The country hosts Volvo’s most significant plants, including the flagship facility in Torslanda.
Torslanda Plant (Gothenburg)
Established in 1964, the Torslanda plant is Volvo’s largest manufacturing facility and serves as the company’s primary production hub. This state-of-the-art factory produces several of Volvo’s most popular models, including the XC60, XC90, and V90 Cross Country. The plant has undergone significant modernization in recent years, incorporating advanced automation and sustainable manufacturing practices.
| Swedish Plant | Location | Established | Models Produced | Production Capacity |
| Torslanda Plant | Gothenburg | 1964 | XC60, XC90, V90 Cross Country | 300,000 units/year |
| Olofström Plant | Olofström | 1969 | Body components | N/A (component factory) |
| Skövde Plant | Skövde | 1927 | Engines | N/A (engine factory) |
| Floby Plant | Floby | 1957 | Brake discs, wheel hubs | N/A (component factory) |
In addition to the Torslanda assembly plant, Sweden is home to several specialized Volvo manufacturing facilities:
- The Olofström Plant specializes in body components and stamping operations
- The Skövde Plant focuses on engine production
- The Floby Plant manufactures brake discs and wheel hubs
These Swedish facilities collectively form an integrated manufacturing ecosystem that supports Volvo’s global production network.
Belgium: Volvo’s European Hub

Ghent Plant
Established in 1965, the Ghent plant in Belgium represents Volvo’s first major manufacturing facility outside of Sweden. This factory has evolved into a crucial production center for the company’s smaller models and electric vehicles.
“The Ghent plant has been transformed into Volvo’s electric vehicle hub in Europe, playing a vital role in our electrification strategy and sustainable manufacturing initiatives.”
The Ghent facility currently produces several key models:
- XC40 (including XC40 Recharge electric variant)
- V60 Cross Country
- C40 Recharge (fully electric)
- EX30 (compact electric SUV)
With a production capacity of approximately 270,000 vehicles annually, the Ghent plant has undergone significant expansion to accommodate Volvo’s growing electric vehicle lineup. The facility employs over 6,500 workers and incorporates advanced manufacturing technologies and sustainable practices.
China: Strategic Manufacturing Expansion

Following Volvo’s acquisition by Chinese automotive group Geely in 2010, the company has significantly expanded its manufacturing presence in China. The country now hosts three major Volvo production facilities, serving both the domestic Chinese market and global export needs.
Chengdu Plant
Opened in 2013, the Chengdu plant was Volvo’s first manufacturing facility in China. This factory produces the S60 sedan and XC60 SUV primarily for the Chinese market, though some vehicles are exported to other Asian countries. The plant has recently begun production of electric vehicles, including the EX90 and EX30 models.
Daqing Plant
The Daqing facility, established in 2014, specializes in producing Volvo’s flagship S90 sedan and its long-wheelbase variant (S90L) designed specifically for the Chinese market. In 2017, the plant began exporting S90 sedans to Europe via a unique rail network, highlighting Volvo’s innovative approach to global logistics.
Luqiao Plant
The Luqiao facility, often referred to as the “CMA Super Factory,” began operations in 2019. This plant focuses on producing vehicles based on Volvo’s Compact Modular Architecture (CMA), including the XC40 and various Polestar models. The facility represents a collaborative approach, as it also manufactures vehicles for Lynk & Co, another brand under the Geely umbrella.
Collectively, Volvo’s Chinese manufacturing facilities have a production capacity exceeding 300,000 vehicles annually. These plants incorporate the same quality standards and manufacturing processes used in Volvo’s European facilities, ensuring consistent product quality across all markets.
United States: Volvo’s American Manufacturing Base

Charleston Plant (Ridgeville, South Carolina)
Volvo’s manufacturing presence in the United States is centered around its state-of-the-art plant in Ridgeville, South Carolina, near Charleston. Opened in 2018, this facility represents a $1.1 billion investment and underscores Volvo’s commitment to the North American market.
The Charleston plant initially focused on producing the S60 sedan, but production of this model ended in 2024 to make way for the company’s electric vehicle strategy. The facility now manufactures the all-electric EX90 SUV, positioning it as a key component of Volvo’s global electrification efforts.
Volvo Charleston Plant Facts:
- 2.3 million square feet facility on 1,600 acres
- Production capacity: 150,000 vehicles annually
- Features body shop, paint shop, final assembly, and vehicle processing center
- Home to Volvo Car University and Volvo Car South Carolina Technical Center
- Currently produces the Volvo EX90 electric SUV and Polestar 3
The Charleston facility employs approximately 1,500 people and incorporates advanced manufacturing technologies, including extensive automation and sustainable production practices. The plant’s focus on electric vehicle production aligns with Volvo’s commitment to have 50% of its global sales volume consist of fully electric cars by 2025.
Other Manufacturing Locations
Beyond its major production hubs in Sweden, Belgium, China, and the United States, Volvo maintains manufacturing operations in several other countries to serve regional markets efficiently.
Malaysia

Volvo’s manufacturing presence in Malaysia dates back to 1967, making it the company’s first production facility in Asia. The Shah Alam plant, operated by Volvo Car Manufacturing Malaysia (VCMM), produces several models for the Southeast Asian market, including the XC40, XC60, XC90, S60, S90, and C40 Recharge. This facility has evolved from an assembly operation to a full manufacturing plant, supporting Volvo’s strong position in the Malaysian automotive market.
India
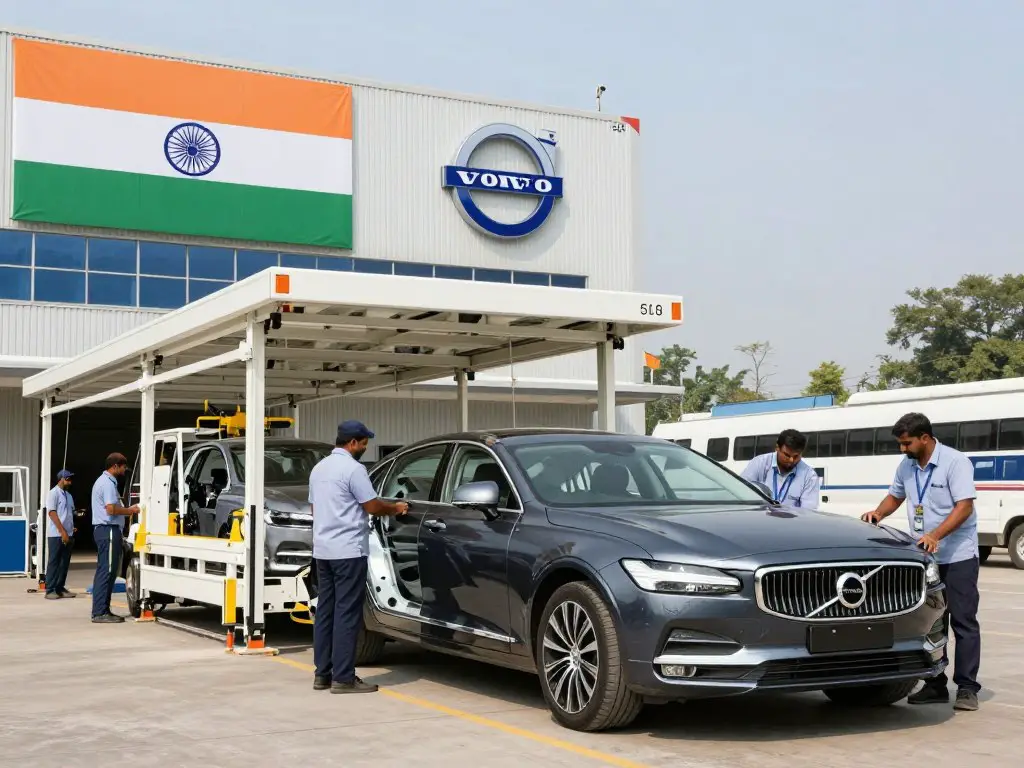

Volvo established its Indian manufacturing operations in Bangalore in 2007. Initially focused on assembly operations, the facility has expanded to include more comprehensive manufacturing capabilities. The Bangalore plant produces the XC90, S60, XC60, and S90 models for the Indian market, allowing Volvo to compete more effectively with other luxury automotive brands in this rapidly growing economy.
Netherlands (Historical)
From 1975 to 2004, Volvo operated the Born Plant in the Netherlands, known as Netherlands Car (NedCar). This facility produced various Volvo models, including the Volvo 66, before being sold to Mitsubishi Motors in 2001. While no longer part of Volvo’s current manufacturing network, this historical facility played an important role in the company’s European production strategy.
Volvo’s Global Manufacturing Strategy

Volvo’s approach to global manufacturing reflects the company’s strategic vision and commitment to sustainability, quality, and innovation. Several key principles guide Volvo’s manufacturing network:
Regional Production for Regional Markets
Volvo strategically locates manufacturing facilities to efficiently serve major markets. This approach reduces logistics costs, minimizes environmental impact from transportation, and allows the company to respond more quickly to regional market demands. The establishment of plants in China and the United States exemplifies this strategy, enabling Volvo to produce vehicles closer to their intended markets.
Consistent Global Quality Standards
Despite its distributed manufacturing footprint, Volvo maintains consistent quality standards across all facilities. The company implements standardized production processes, quality control measures, and training programs to ensure that a Volvo vehicle delivers the same experience regardless of where it was manufactured. This commitment to quality uniformity supports the brand’s premium positioning in the global automotive market.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainability is a core component of Volvo’s manufacturing strategy. The company aims to achieve climate-neutral manufacturing operations by 2025 as part of its broader environmental goals. Initiatives include:
- Powering plants with renewable energy (already achieved at Torslanda, Skövde, and Chengdu)
- Implementing circular economy principles to minimize waste
- Reducing water consumption and emissions
- Optimizing logistics to minimize transportation-related environmental impact

Flexibility and Adaptability
Volvo designs its manufacturing facilities to be flexible and adaptable, capable of producing multiple models on the same production line. This approach allows the company to respond quickly to changing market demands and efficiently introduce new models. The transition to electric vehicle production at plants like Charleston and Ghent demonstrates this flexibility in action.
Future Outlook: Electrification and Expansion

Volvo’s manufacturing footprint continues to evolve as the company pursues its ambitious electrification goals. By 2030, Volvo aims to become a fully electric car company, which will require significant transformations across its global production network.
Electric Vehicle Production Expansion
Volvo is investing heavily in adapting its existing plants for electric vehicle production while also considering new facilities dedicated to EV manufacturing. The Ghent plant in Belgium has already been transformed into an electric vehicle hub, while the Charleston facility in the United States is now focused on producing the EX90 electric SUV.
Battery Production and Partnerships
To support its electric vehicle strategy, Volvo is developing battery production capabilities and forming strategic partnerships. The company has established a joint venture with Northvolt to develop and produce battery cells specifically for Volvo vehicles. A new battery manufacturing plant is planned near Gothenburg, Sweden, further strengthening the company’s vertical integration in electric vehicle production.
Conclusion: A Truly Global Manufacturer
Volvo Cars has successfully transformed from a Swedish automotive company into a truly global manufacturer with production facilities spanning 7 countries across Europe, Asia, and North America. This extensive manufacturing network enables Volvo to efficiently serve markets worldwide while maintaining the quality, safety, and innovation that define the brand.
From its historical roots in Gothenburg, Sweden, to its newest facilities in Charleston, USA, and Luqiao, China, Volvo’s manufacturing plants represent the company’s evolution and its vision for the future. As Volvo continues its journey toward full electrification and sustainable operations, its global manufacturing footprint will remain a critical asset in achieving these ambitious goals.
How many countries have Volvo manufacturing plants?
Volvo Cars currently operates manufacturing facilities in 7 countries: Sweden, Belgium, China, the United States, Malaysia, India, and the Netherlands (historical). These plants collectively produce over 700,000 vehicles annually for markets worldwide.
Which Volvo models are made in the United States?
Volvo’s Charleston plant in South Carolina currently produces the all-electric EX90 SUV and the Polestar 3. Previously, the facility manufactured the S60 sedan, but production shifted to focus on electric vehicles in 2024.
Are all Volvo cars made in Sweden?
No, while Sweden remains Volvo’s home country and hosts several key manufacturing facilities, Volvo cars are produced in 7 countries worldwide. Different models are manufactured at specific plants based on market demand and strategic considerations.