Welcome. This short guide gives clear, professional steps for safely restoring power in Volvo cars and other vehicles. It covers 12V systems, hybrid setups, and basic EV notes so drivers of many models know what to expect.
Safety first. Begin with the charger switched off and attach the positive clamp, then the negative. Secure connections, set the charger per its manual, and allow several hours for a low-voltage battery to recover.
Expect routine maintenance needs: most car battery units last about five years and can drain from lights or accessories left on. Battery fluid can be corrosive, so avoid contact with skin and clothing.
This introduction previews practical tips on identifying terminals, timing a safe recharge, and when professional service is the smarter choice. Whether you explore Volvo ownership or plan upgrades for new Volvo tech, this guide keeps instructions direct and reliable.
Key Takeaways
- Start with the charger off and attach positive then negative clamps.
- Allow several hours for a full top-up on low-voltage batteries.
- Wear protection and avoid contact with corrosive battery fluid.
- Hybrid and EV systems differ; know your vehicle’s specs.
- Seek professional service if charging problems persist.
Understand Your Volvo Battery: 12V, Hybrid, and Fully Electric Basics
Different Volvo power systems use distinct battery setups and demand different care.
12V role. The small 12V car battery provides starter current for the engine and powers accessories when the motor is off. You may need an external charge if cranking becomes slow, dashboard lights dim, or electronics struggle.
Aging and use. Many lead-acid batteries last about five years. Repeated drains from lights or the radio can leave a vehicle unable to start and signal the need for recharge or replacement.
Hybrid and EV essentials
Hybrid architecture. Hybrids combine a gasoline engine with one or more electric motors and a high-voltage pack. They still use a 12V auxiliary battery for control systems and infotainment.
EV packs and kWh. Fully electric models use large lithium-ion packs measured in kilowatt-hours. More kWh usually means greater range; for example, ~40 kWh can deliver roughly 150 miles, while larger packs exceed 300 miles on certain configurations.
| System | Main Battery | Secondary 12V Role | Typical Charge Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 12V lead-acid | Starts engine, runs accessories | Charger/alternator |
| Hybrid (e.g., XC90 plug-in) | High-voltage pack + 12V | Controls, locks, displays | Level 1, Level 2, regen braking |
| Fully electric | Large kWh lithium-ion pack | Boots systems, security | 120V, Level 2, DC fast |
Regenerative braking. Lifting off the throttle lets the motor recover motion energy and feed it back into the high-voltage pack. This extends range and reduces dependency on external charging during city driving.
How to Charge a Volvo Battery? Any Model or Battery Type
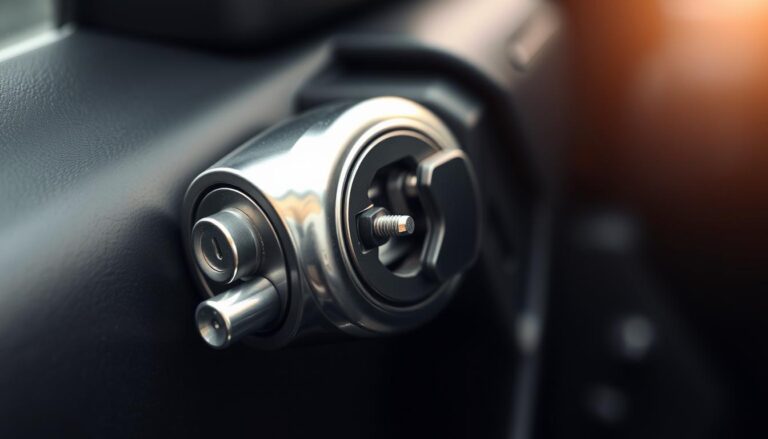
Start with safety: always switch the charger off before you touch clamps and wear eye and hand protection. Keep sparks, open flames, and loose clothing away from the area. Battery fluid is corrosive; avoid skin contact and wash any splashes immediately.

Identify terminals correctly
Find the positive (+) post and the negative (−) post on the car battery. Connect the red clamp to positive and the black clamp to negative. Make sure clamps bite metal and sit clear of moving engine parts.
Connect the battery charger
Confirm the charger is off, then attach clamps as described. Plug the unit into a grounded outlet and select the correct mode or amperage for the car battery. Set a timer per the charger manual and start charging.
Charging duration and monitoring
Low open-circuit voltage batteries typically need about 6–12 hours on a standard battery charger. High-amp boost modes cut time but stress cells and parts.
- Check indicator lights or the display periodically.
- Warm, not hot, casings are normal; stop immediately if you smell burning or see swelling.
- Turn the charger off before removing clamps; remove negative first, then positive.
When to seek professional help
If the engine still cranks slowly, the battery won’t accept a full charge, or systems act erratic, visit a service center for testing. Quality parts, fresh cables, and terminal protectors help long-term reliability. If unsure, get professional service or consult hybridshop specialists for hybrid systems.
Charging Volvo Hybrids and EVs (XC40, EX30, and More): Home, Level 2, and DC Fast
Home outlets, Level 2 units, and public fast stations each serve distinct charging needs. A 120‑volt outlet is convenient for overnight top‑ups but runs slowly. Installing a Level 2 charger at home cuts hours from each session and suits daily routines for many new Volvo owners.

Home charging: outlet vs Level 2
Outlet — uses common household power and works for low daily miles.
Level 2 — installs on a dedicated circuit and reduces dwell time. Consider finance options for a professional install and check specialsVolvo offers when buying a new Volvo.
Public charging and DC fast
DC fast at a station gives rapid top‑ups for road trips. Use it for quick range boosts, not daily fills, to protect long‑term battery health. Move when finished and check network pricing before plugging in.
Range, kWh, and regen
Smaller packs around 40 kWh often yield ~150 miles; larger packs can exceed 300 miles depending on motors and conditions. Regenerative braking returns power while slowing, improving city efficiency on models like the Volvo xc40 Recharge and the Volvo ex30.
- Map reliable stations and arrive with moderate state of charge for best fast‑charge speeds.
- Verify charger compatibility and software updates for optimal charge curves.
- Use Level 2 at home for routine charging; reserve DC fast at a public station for trips.
Conclusion
Finish each charging session with a quick inspection and a short log of what you did. Verify the charger was off when you connected clamps, confirm positive-to-positive and negative-to-negative contacts, set the timer per the device instructions, and allow 6–12 hours for deeply discharged cells when needed.
Safety matters. Avoid corrosive fluid contact, wear protection, and keep approved parts like terminal cleaners and protective boots on hand. Routine care reduces surprises and keeps engines and electronics working across multiple Volvo cars.
If repeated no-starts or strange electrical behavior appears, book time at a trusted service center. Trained technicians at the center or hybridshop specialists can test batteries, diagnose alternators, and replace worn parts. Check specialsVolvo for offers on installs and certified components.